Making Releases Unmodifiable with GitHub’s Immutable Releases
Back to TopTo reach a broader audience, this article has been translated from Japanese.
You can find the original version here.
Introduction
#Last month, Immutable releases became generally available.
With this, you can confirm that a release has not been modified after publication, helping to prevent tampering and accidental changes.
Features of Immutable Releases
#You can refer to the documentation at the following link.
Immutable releases have the following characteristics:
- Git tags cannot be moved or deleted: The Git tags associated with a release are locked to a specific commit and cannot be changed or deleted.
- Release assets cannot be modified or removed: All files attached to a release are protected from modification or deletion.
A release attestation is automatically generated, allowing you to verify the release tag, commit SHA, assets, and more.
When Immutable releases are enabled, even if you delete that repository and create a new repository with the same name, you cannot reuse tags associated with immutable releases from the original repository. This is a powerful protection feature.
Trying It Out
#I tried setting this up in the repository of the unofficial Cosense app sbe that I maintain.
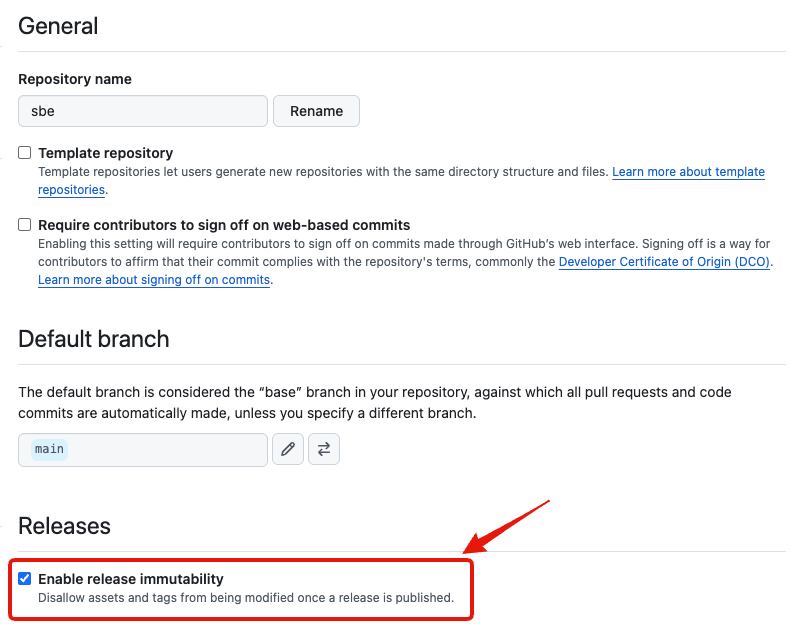
Immutable releases can be configured at the repository or organization level.
Once a release is published, even repository committers cannot modify it, so the following workflow using draft releases is recommended:
- Create a draft release
- Attach all assets to the draft release
- Promote the draft release to an official release
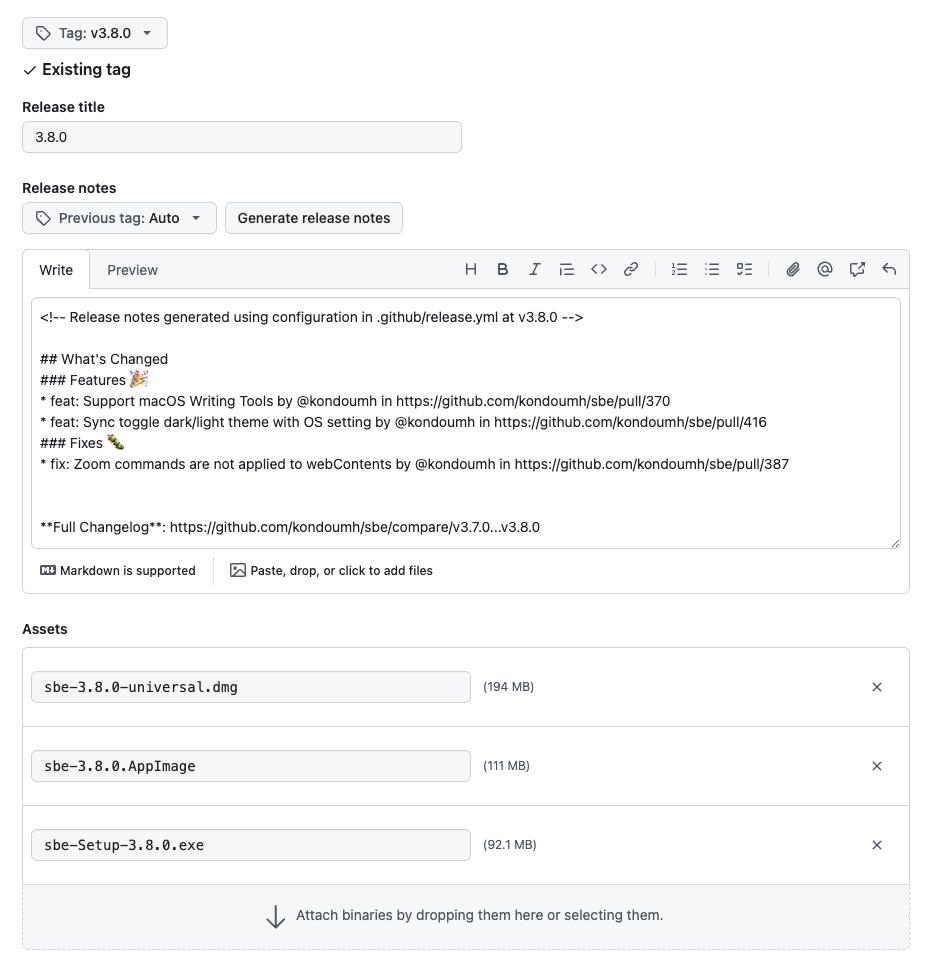
Since changes had accumulated for sbe, I created a release draft following these best practices.
The saved draft release is still private and can be modified.
In this app's release workflow, we trigger release creation when a tag is created.
We use an Action called softprops/action-gh-release. It also attaches release artifacts. By setting prerelease to true, it creates a draft release.
- name: Publish
uses: softprops/action-gh-release@v2
with:
files: |
dist/**/*.exe
dist/**/*.deb
dist/**/*.AppImage
dist/**/*.dmg
prerelease: true
After checking the attached files and changes, publish the release.
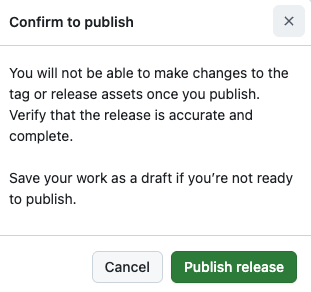
When Immutable releases are enabled, a confirmation dialog appears.
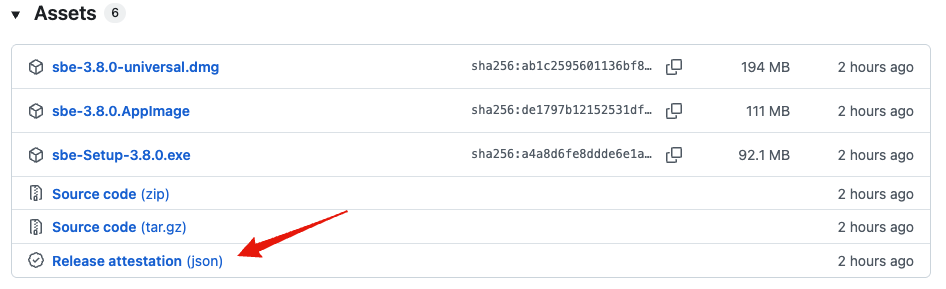
The published release is marked as Immutable.
A JSON file of the release attestation is also added to the assets.
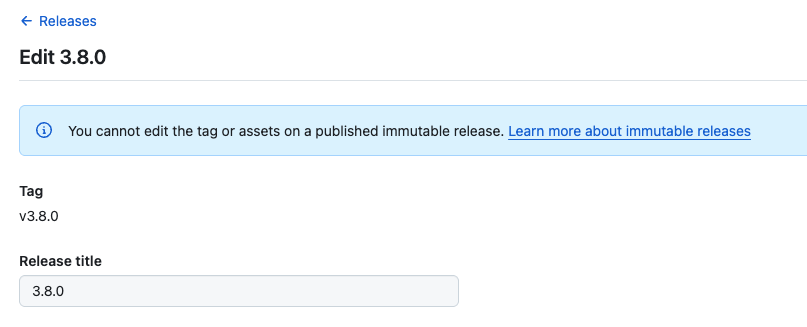
In the editing screen, you can modify the release description and so on, but a message indicates that tags and assets cannot be edited.
Verifying a Release
#Users can verify releases made immutable by Immutable releases using the GitHub CLI.
To verify that a release exists and is immutable, run the release verify command in the directory of a cloned repository.
gh release verify RELEASE-TAG
When verifying the v3.8.0 release of sbe, it reads and displays the attestation using the GitHub API.
$ gh release verify v3.8.0
Resolved tag v3.8.0 to sha1:1f3f380d33f022230046a3200a67950ea027c8a1
Loaded attestation from GitHub API
✓ Release v3.8.0 verified!
Assets
NAME DIGEST
sbe-3.8.0-universal.dmg sha256:ab1c2595601136bf82aa7594d48bc764fe6f226ed1071c52441eb531f34e0252
sbe-3.8.0.AppImage sha256:de1797b12152531df71e78519d660e32e1a79dca203bc3201d85b2facfe4b5a9
sbe-Setup-3.8.0.exe sha256:a4a8d6fe8ddde6e1a2005a29d7e2759511cb537427e4a0ff03440c5e9f48fb94
To verify that a local artifact exactly matches a release asset, use the release verify-asset command.
gh release verify-asset RELEASE-TAG ARTIFACT-PATH
I tried downloading and verifying the macOS universal installer binary from the release assets.
$ gh release verify-asset v3.8.0 ~/Downloads/sbe-3.8.0-universal.dmg
Calculated digest for sbe-3.8.0-universal.dmg: sha256:ab1c2595601136bf82aa7594d48bc764fe6f226ed1071c52441eb531f34e0252
Resolved tag v3.8.0 to sha1:1f3f380d33f022230046a3200a67950ea027c8a1
Loaded attestation from GitHub API
✓ Verification succeeded! sbe-3.8.0-universal.dmg is present in release v3.8.0
The attestation of assets uses Sigstore’s signing technology. This technology enables verification of the software’s provenance, improving the security of the software supply chain. Although it’s an older article, it’s introduced in the following post.
Conclusion
#That concludes the introduction to Immutable releases. For OSS projects with a significant number of users, adopting Immutable releases is recommended.
When using third-party Actions in GitHub Actions, you sometimes pin not only by version but also by commit hash to avoid unintended changes. It would be reassuring for users if more Actions adopted Immutable releases.